
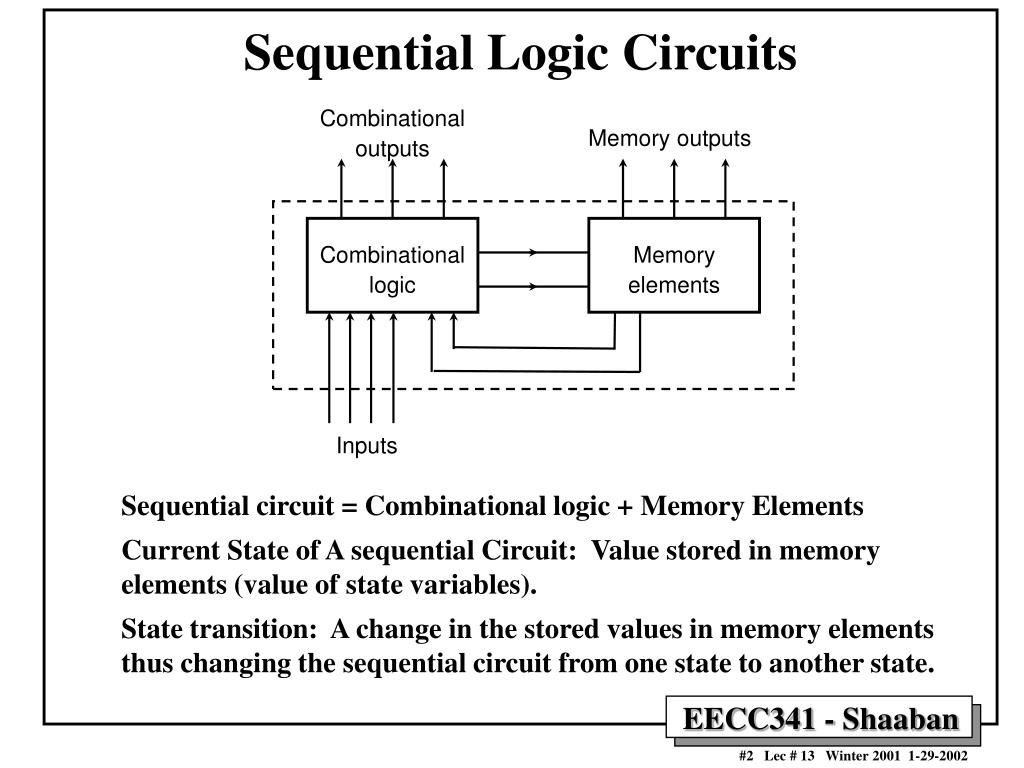
Sequential circuits receive binary information via extrinsic inputs. The binary information stored within memory elements at a given period of time, explicates the state of a sequential circuit. Memory elements are devices which have a capacity to store binary information within it. A sequential circuit comprises a feedback path between combinational circuit and memory elements, as has been represented by a block diagram of the sequential circuit in figure 5.1. flip-flop is a basic chip which is being used on a sequential circuit. In other words, basic feature of a sequential circuit has been memory or sequential circuits are a type of circuits, which have a capacity to store binary numbers.

these circuits are manufactured through the assistance of different logic gates), whereas sequential logic circuits are used in timing and memory devices and flip-flop serve as a building block on them. In combinational logic circuits (about which we have already read in the previous chapters) gates serve as basic building block (i.e. The following types expounds the difference between operations of these two types of logic circuits. Logic circuit is normally divided into two types. Flip-flops are mostly used in the construction of registers, counters and timers etc. Flip-flop is a basic memory element and it is also known as a bistable multi – vibrator. It is a prominent feature of a flip-flop that as long as status of its input signal is not changed, it remains indefinitely on any one of the afore – mentioned two states (as long as power is transmitted on the circuit). In other words, a digital element, which can store only one bit of a binary data, is known as a flip-flop. This process is experimental and the keywords may be updated as the learning algorithm improves.Flip-Flop Combinational logic circuits and Sequential logic circuits- Flip-flop is a memory element, which can store at a time either binary 1 or binary 0. These keywords were added by machine and not by the authors. The bits in register A remain after the operation. If the output of register A is connected to the input of register B, the presence of a clock at the input can transfer the bits from register A to register B. Precisely, an eight-bit register can store eight bits, a 16-bit register can store 16 bits, and a 32-bit register can store 32 bits. The length of a register is the number of bits that can be stored. Thus, a register is used to store many bits where each ff is a one-bit storage cell in a register. By grouping an ordered set of flip-flops, we obtain a register. Thus, the data inputs and clock input jointly control the timing of the change in its output voltage. A synchronous ff has a clock input in addition to its data inputs.
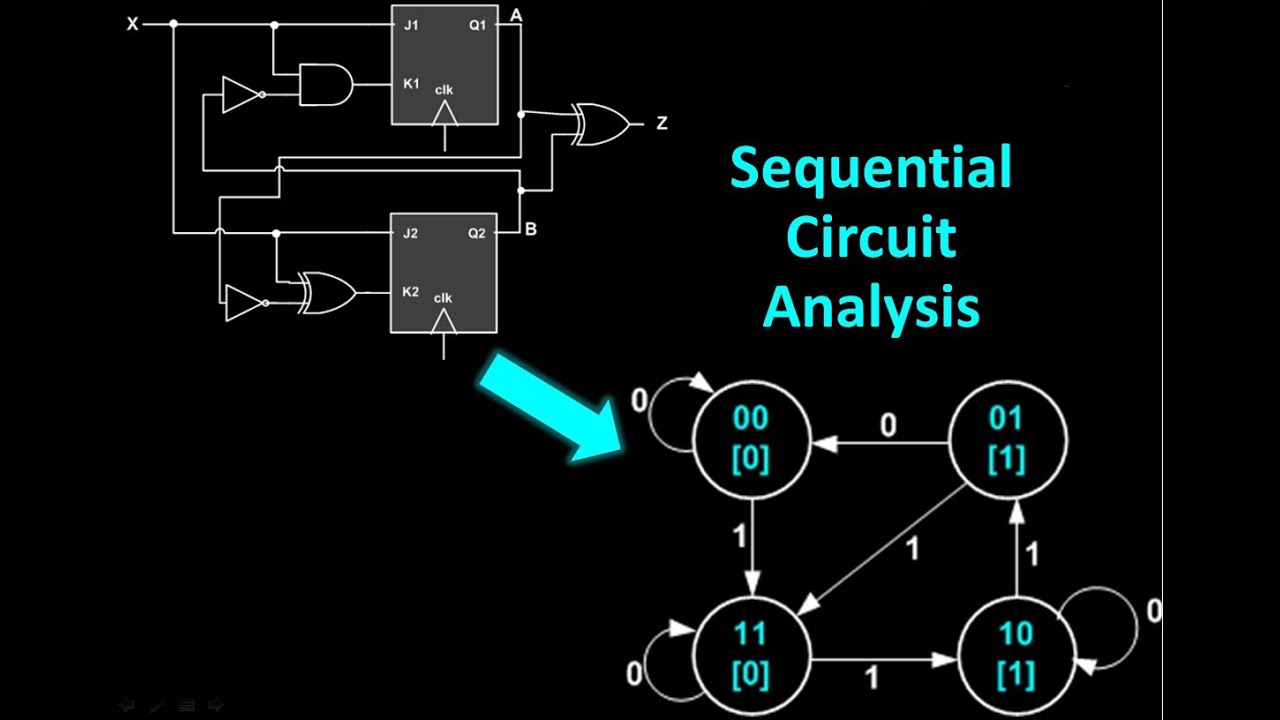
An asynchronous ff requires no clock, but a synchronous one does. If the output of an ff changes as its input changes but is controlled by a clock, it is a synchronous ff. If the output of an ff changes as soon as its input changes, it is called an asynchronous ff. In concept, a sequential circuit uses logic gates to provide the control functions, and it uses flip-flops to store the digital signals.
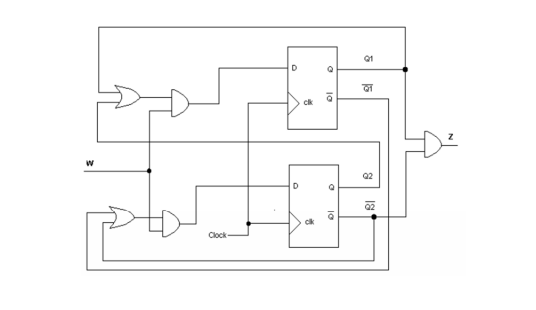
Such a device is used to store one bit of information. One output indicates the true variable of the output, and the other indicates its complement. A flip-flop (ff) is a bistable device that has two outputs. A sequential circuit consists of logic gates and flip-flops.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
